Breakthrough in Energy Storage: Flexible Supercapacitors Developed with Conducting Polymer and Nanostructured Oxides
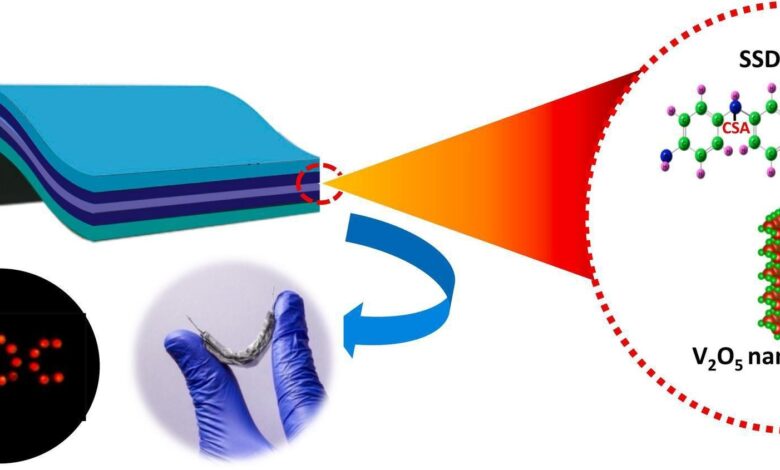
Scientists at the Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices Group within the Department of Physics at Sanatana Dharma College in Alappuzha have achieved a significant milestone in energy storage. They have developed a groundbreaking hybrid electrode-based flexible symmetric supercapacitor, offering an efficient solution for energy storage with impressive electrochemical properties, cycle stability, and high energy density.
Key Highlights:
- A Quest for Efficient Energy Storage: With the increasing demand for energy solutions, the pursuit of efficient and stable electrode materials for energy storage has been at the forefront of scientific research. Researchers in the field of supercapacitor electrodes aim to elevate energy density values, drawing closer to those achieved by conventional batteries.
- Conducting Polymers: Conducting polymers have garnered attention as pseudocapacitive materials with diverse applications and the potential to meet the fundamental requirements for supercapacitor electrodes.
- The Breakthrough: Researchers at the Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices Group have developed a flexible symmetric supercapacitor with a hybrid electrode structure that stands out due to its remarkable electrochemical properties, cycle stability, and high energy density.
- Unique Hybrid Electrode: The binder-free hybrid electrode incorporates high-molecular-weight polyaniline (PANi) created through self-stabilized dispersion polymerization and vanadium pentoxide nanostructures prepared using a microwave-assisted method. Unlike conventional PANi-based electrodes, these electrodes are prepared from a dispersion of PANi with a secondary dopant in m-cresol.
- Synergistic Effect: The combination of high-molecular-weight PANi with nanostructured V2O5 effectively addresses the limitations of these individual materials and demonstrates a synergistic effect, leading to superior electrochemical characteristics, very high energy density, and cycling stability.
- Impressive Performance: The flexible supercapacitor device constructed with these electrodes exhibits remarkable electrochemical characteristics with the highest energy density and cycling stability values reported for supercapacitors using aqueous electrolytes.
- Scientific Collaboration: This research was conducted at SD College with support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST) through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) program and has been recently published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
This breakthrough in flexible supercapacitors opens new doors for efficient energy storage solutions, offering enhanced performance and stability for a wide range of applications in the ever-evolving energy landscape.




